EPF India - Complete Guide to EPFO and EPF in India
India is one of the fastest growing major economy in the world. Key factors behind this growth are - a big pool of working-age population; rising education and engineering skill levels; and a rapidly growing middle class. However, the downside of having a massive population of more than 121 crores is that India continues to face the challenges of poverty, corruption, malnutrition, and inadequate public healthcare. This is where the Indian Government tries to step in with various social security schemes like EPF India, ESIC, etc. to protect a worker and his family against work or health related eventualities.
The social security system in India faces a major challenge from the unorganized sector. The unorganized sector does not have an organizational structure and does not come under the labour law purview making it difficult to pass on the benefits of social security schemes to workers. Examples of unorganized sectors are landless agricultural labourers, small and marginal farmers, rural artisans, manual labourers in construction, street vendors, hawkers, etc. For the organized sector, social security is provided through the instrumentality of Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) and Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC).
EPF India, EPFO - Major Social Security Scheme in India
India's Employees Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) is one of the largest social security plans in India covering over 12 crore EPF Members and their families. EPFO expends to the entire country, except in the State of Jammu and Kashmir covering over 8 lac establishments. The total investment corpus as on 31st March, 2014 amounts to ₹ 7,30,393/- crores. EPFO falls under the control of the Indian Government through the Ministry of Labour and Employment. The EPFO's apex decision making body is the Central Board of Trustees (CBT).
EPFO India runs three different schemes for its members -
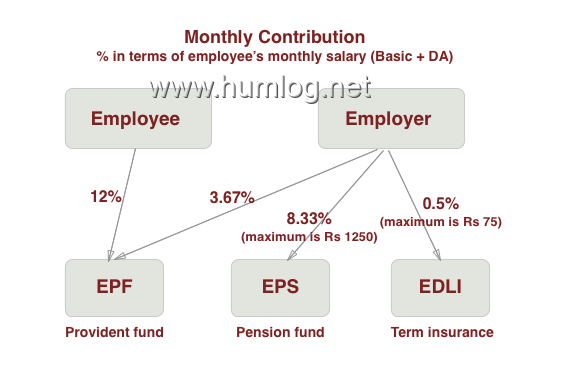
- Employees' Provident Funds Scheme (EPF) - Provident Fund
- Employees' Pension Scheme (EPS) - Pension
- Employees' Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme (EDLI) - Term Insurance
These 3 schemes are interlinked and clubbed together to be known as EPF India. So if an employee becomes a member of EPF, he is automatically registered in the pension (EPS) and insurance (EDLI) schemes too. The aim of these schemes is to grant EPFO members and their families financial security for old age, disability, and support in case the primary breadwinner dies.
EPF India - Employee Provident Fund Scheme
The EPF India scheme, enacted in the year 1952, is known as the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Act, 1952. The EPF scheme applies to private organizations with at least 20 employees. For workers having a monthly salary (Basic + DA) of less than Rs 15000/-, it is mandatory to get enrolled in EPF scheme. Otherwise it is not mandatory but it is a standard and best practice to invest in EPF all across the working population.
The Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) is a corpus of funds in which both you and your employer contribute a fixed amount every month. Your contribution goes only into the EPF scheme / account while the employer contribution goes into all three schemes - EPF, EPS and EDLIS.
EPF is one of the best fixed return schemes available in India due to five reasons:
- Very good interest rates
- Interest earned is tax free
- Total amount withdrawn at maturity is tax free.
- Principal amount is exempted from income tax upto 1.5Lakh (section 80C)
- Partial withdrawal is allowed before maturity for emergency needs.
EPF India Online services
Over the years, the volume of service rendered to subscribers as well as investments made by EPFO have grown many folds. EPFO has focused its effort on automation of the work processes to achieve better efficiency and improved service delivery to its members.
Following are some main online services:
- EPF UAN member portal
- EPF UAN Employer portal
- EPF balance check
- EPF withdrawl
- EPF UAN Login and UAN Activation
EPF India Interest Rates and return on investment
EPF India Gov Site for Employers
EPF India has come with a unified portal to allow employers easily manage their activities for employee epf contribution and ecr challan and it is available at EPF Employer Portal